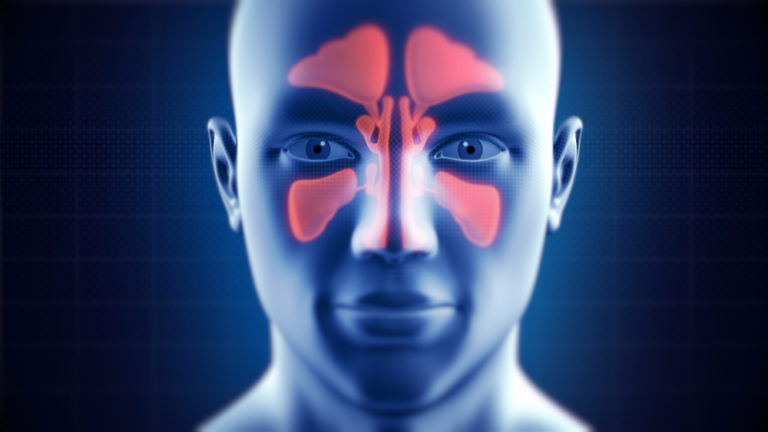
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are common conditions affecting millions of people worldwide. They occur when the nasal cavities become swollen and inflamed, leading to symptoms like congestion, headache, facial pain, and a runny nose. One frequently asked question is: Are Sinus Infections Contagious? Understanding the nature of sinus infections and their causes is crucial in addressing this concern.

Types of Sinus Infections
Sinus infections can be classified into two main types acute and chronic.
Acute Sinusitis:
This type is short-term, often triggered by a common cold and typically lasts less than four weeks. Symptom include facial pain, nasal congstion, nasal discharge, and sometimes fever.
Chronic Sinusitis:
This type persists for more than 12 weeks despite treatment and can last for months or even years. Symptoms are similar to acute sinusiti but may also include a decreased sense of smell, fatigue, and ear pain.
Causes of Sinus Infections
Sinus infections can be caused by various factors, including:
- Viruses: The most common cause of sinus infections is viral infections such as the common cold. Viral sinusitis is usually not contagious.
- Bacteria: Bacterial infections can cause sinusitis particularly if symptoms persist for more than ten days or worsen after initially improving
- Fungi: Fungal sinusitis is less common and typically affects people with weakened immune systems or allergies.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation and blockage of the sinuses, leading to sinus infections.
- Environmental Factors: Pollutants, smoke and irritants can contribute to sinus infections.
Are Sinus Infections Contagious?
The contagiousness of sinus infections depends on the underlying cause:
Viral Sinus Infections:
Viral sinusitis is not contagious. However, the viruses that cause the common cold, which can lead to sinus infections, are highly contagious. These viruses spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Bacterial Sinus Infections:
Bacterial sinusitis itself is not contagious. However, the bacteria causing the infection can spread if the infected individual has a concurrent respiratory infection.
Fungal Sinus Infections:
Fungal sinusitis is not contagious and is typically related to environmental exposure or an individual’s immune status.
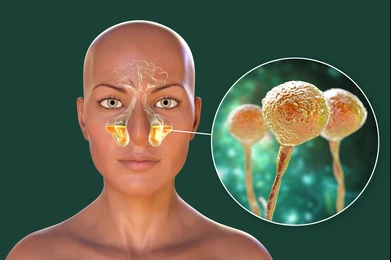
Allergic Sinusitis:
Sinus infections caused by allergies are not contagious. They result from the body’s response to allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander.
Preventing Sinus Infections
While sinus infections themselves may not always be contagious, preventing the spread of the underlying causes, such as viruses, is essential. Here are some preventive measures:
- Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing with soap and water helps reduce the spread of viruses and bacteria. Avoid touching your face, especially your nose and mouth, with unwashed hands.
- Avoid Close Contact: Stay away from individuals who have colds or other respiratory infections. If you are sick, limit your contact with others to prevent spreading the infection.
- Use Tissues: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when you cough or sneeze. Dispose of used tissues properly and wash your hands afterward.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A strong immune system can help prevent infections. Eat a balanced diet, get regular exercise, and ensure adequate sleep.
- Manage Allergies: If you have allergies, work with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively. This can reduce the risk of developing sinus infections.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps keep the mucus in your sinuses thin, reducing the risk of blockages and infections.
Treatment of Sinus Infections
Treatment for sinus infections depends on the cause:
- Viral Sinusitis: Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications can help relieve symptoms. Decongestants and saline nasal sprays may also provide relief.
- Bacterial Sinusitis: Antibiotics may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is confirmed. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Fungal Sinusitis: Antifungal medications and, in some cases, surgery may be required to treat fungal sinus infections.
- Allergic Sinusitis: Managing the underlying allergies through medications and avoiding allergens can help prevent and treat sinus infection
Advice from Dr. Jennifer Collins, a Renowned ENT Specialist

To gain further insights into managing sinus infections we consulted Dr. Jennifer Collins, a well-known Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) specialist with years of experience in treating sinus-related issues. Dr. Collins emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach to sinus health:
- Early Intervention: It’s crucial to address sinus infection symptoms early. Over-the-counter treatments like saline nasal sprays and decongestants can be effective in reducing symptoms. If symptoms persist beyond 10 days or worsen, consult a healthcare provider.
- Nasal Irrigation: Nasal irrigation using a saline solution can help keep the nasal passages clear and reduce inflammation. It’s a simple, effective method to alleviate congestion and improve sinus health.
- Avoid Irritants: Environmental irritants such as smoke, pollutants, and strong odors can exacerbate sinusitis. Avoiding these irritants and maintaining a clean living environment can significantly reduce the risk of sinus infections.
- Stay Hydrated: Hydration is key. Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin the mucus, promoting better drainage and reducing the risk of blockages.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you have recurrent or chronic sinus infections, it’s important to seek professional advice. A specialist can identify underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments, which may include medications or surgical interventions.
When to See a Doctor
Most sinus infections resolve on their own without medical intervention. However, you should see a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist for more than ten days.
- Symptoms worsen after initially improving.
- You experience severe facial pain, sweling, or a high fever.
- You have recurrent sinus infections.
A healthcare provider can diagnose the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
In summary, sinus infections themselves are generally not contagious, but the viruses and bacteria that can lead to sinus infections may be. Understanding the causes and preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing sinus infections and spreading underlying infections to others. Health Ideas, such as maintaining good hygiene, managing allergies, and seeking medical advice when necessary, are essential steps in managing sinus health.
By taking these precautions and being aware of the nature of sinus infections, individuals can better protect themselves and others from the discomfort and potential complications associated with sinusitis.


No Comment! Be the first one.