Staphylococcus lugdunensis is a coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CoNS) that has gained attention due to its pathogenic potential, often resembling the more notorious Staphylococcus aureus in its ability to cause serious infections. Unlike other CoNS, which are typically considered less virulent, S. lugdunensis has demonstrated a unique propensity for causing severe conditions such as endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and skin and soft tissue infections. This article delves into the characteristics pathogenicity clinical implications, diagnosis, and treatment of S. lugdunensis aiming to provide a thorough understanding of this significant microorganism.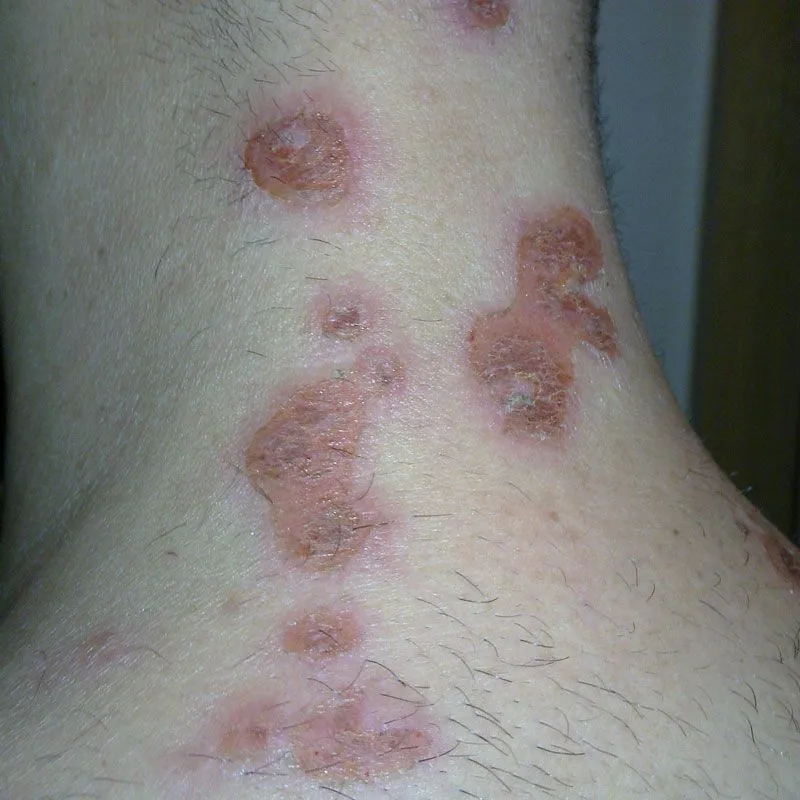
Characteristics of Staphylococcus lugdunensis
- lugdunensis was first identified in 1988 and is named after the city of Lyon (Lugdunum in Latin) in France. It is a Gram-positive, coagulase-negative bacterium that is part of the normal skin flora. However, its clinical significance lies in its pathogenic potential which is comparable to that of S. aureus
| Characteristic | Description |
| Morphology | Gram-positive cocci in clusters |
| Colony Appearance | Creamy to yellow colonies on standard media |
| Catalase Test | Positive |
| Coagulase Test | Negative |
| Clumping Factor | Present |
| Biofilm Formation | Yes |
- Virulence Factors: S. lugdunensis possesses several virulence factors, including biofilm formation, adherence factors, and enzymes such as lipases and proteases. Its ability to form biofilms on medical devices contributes to its pathogenicity, making infections challenging to treat.

Pathogenicity and Clinical Implications
- lugdunensis is associated with a variety of infections ranging from skin and soft tissuee infections to life-threatening conditions such as endocarditis.
| Type of Infection | Clinical Features |
| Skin and Soft Tissue | Abscesses, cellulitis, wound infections |
| Endocarditis | Fever, heart murmur, embolic phenomena |
| Bone and Joint | Osteomyelitis, septic arthritis |
| Bloodstream | Bacteremia, sepsis |
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: S. lugdunensis is frequently isolated from abscesses, cellulitis, and wound infections. It is often mistaken for S. aureus due to its aggressive behavior and the severity of the infections it causes.- Endocarditis: One of the most serious infections caused by S. lugdunensis is endocarditis, which can affect both native and prosthetic heart valves. The clinical presentation is similar to that caused by S. aureus, including fever, heart murmur, and embolic phenomena. The mortality rate for S. lugdunensis endocarditis is high, necessitating prompt and aggressive treatment.
- Bone and Joint Infections: S. lugdunensis can cause osteomyelitis and septic arthritis, particularly following trauma or surgery. These infections are characterized by pain, swelling, and decreased mobility of the affected joint or bone.
- Bloodstream Infections: Bacteremia caused by S. lugdunensis is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. It often originates from an infected intravascular device or secondary to another focus of infection.
Diagnosis
Accurate and timely diagnosis of S. lugdunensis infections is crucial for appropriate management. The identification process involves several stepss
| Diagnostic Method | Details |
| Clinical Presentation | Similar to S. aureus infections |
| Culture | Creamy to yellow colonies on standard media |
| Biochemical Tests | Catalase-positive, coagulase-negative |
| Molecular Methods | PCR, MALDI-TOF MS |
Figure 1: Identification Flowchart for S. lugdunensis
Sample Collection -> Culture -> Biochemical Tests (Catalase, Coagulase) -> Clumping Factor Test -> Molecular Identification (PCR, MALDI-TOF MS)
Antimicrobial Susceptibility
- lugdunensis typically shows susceptibility to a range of antibiotics, including beta-lactams. However, resistance patterns can vary, and susceptibility testing is recommended to guide therapy.
| Antibiotic | Susceptibility |
| Penicillin | Variable |
| Cephalosporins | Generally susceptible |
| Methicillin | Resistance reported |
| Vancomycin | Susceptible |
| Linezolid | Susceptible |

Treatment
The treatment of S. lugdunensis infections depends on the site and severity of the infection, as well as the antimicrobial susceptibility profile.
- Antibiotic Therapy: S. lugdunensis is generally susceptible to beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillin and cephalosporins. However, methicillin resistance has been reported, necessitating the use of alternative agents such as vancomycin or linezolid for resistant strains. Combination therapy may be required for severe infections such as endocarditis.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of abscesses, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove infected tissue or foreign material. Drainage of abscesses and debridement of infected bones are common procedures.
- Management of Medical Devices: Infections related to medical devices, such as catheters and prosthetic valves, often require removal or replacement of the device in addition to antibiotic therapy.
Figure 2: Treatment Algorithm for S. lugdunensis Infections
Infection Site -> Assess Severity -> Obtain Culture -> Susceptibility Testing -> Antibiotic Therapy -> Surgical Intervention (if needed) -> Follow-up
Prevention and Control
Preventing S. lugdunensis infections involves standard infection control practices, especially in healthcare settings.
- Hand Hygiene: Rigorous hand hygiene practices among healthcare workers are essential to prevent the spread of S. lugdunensis.
- Aseptic Techniques: Proper aseptic techniques during surgical procedures and the insertion of medical devices can reduce the risk of infection.
- Surveillance: Active surveillance for S. lugdunensis in healthcare settings can help identify outbreaks and implement control measures promptly.
Conclusion
Staphylococcus lugdunensis, though a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci, exhibits pathogenic traits akin to S. aureus, making it a significant cause of serious infections. Understanding its characteristics, pathogenicity, and clinical implications is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Health Ideas that focus on advancements in molecular diagnostic methods and a better grasp of its virulence factors can empower healthcare providers to improve outcomes for patients affected by this formidable pathogen. Continued research and vigilance in infection control practices are essential to mitigate the impact of S. lugdunensis in both community and healthcare settings.


No Comment! Be the first one.